US battery storage capacity is poised for a record year in 2024 with Texas and California continuing to lead in the US in new additions, after installations reached a new record last quarter.
“Like solar, batteries are poised for a record year of installations as well,” Willette said. “As renewables increasingly penetrate the grid and emissions standards become more stringent, the role batteries play in enhancing grid reliability is being further emphasized.”
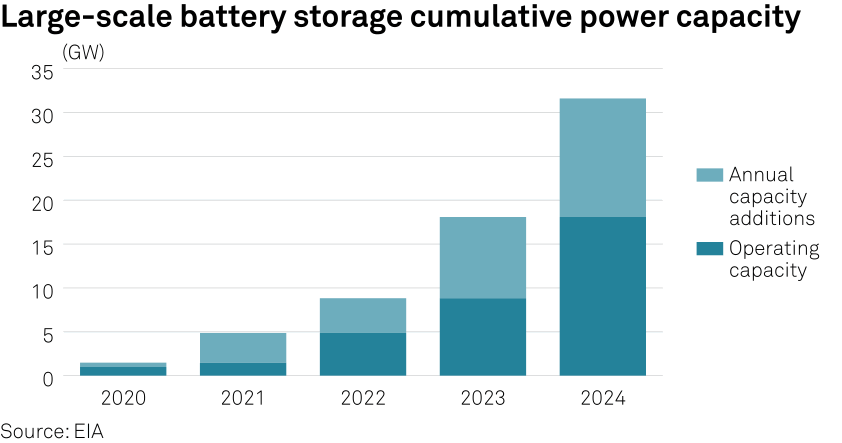
The US Energy Information Administration expects new solar generating capacity to be accompanied by 9 GW of new battery storage capacity in 2023, doubling the total amount compared with what was operating at the end of 2022.
Prior to the Inflation Reduction Act, batteries only qualified for federal tax credits if they were located alongside solar. But with the passage of the IRA, standalone battery systems now qualify for the investment tax credit, Willette said. In conjunction with the IRA, battery system capital costs continue to decline, further improving the economics of the tech.
The battery storage added in Q4 is expected to be roughly 4.5 GW, according to an S&P Global compilation of various government filings.
Regional breakdown
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas and California continue to dominate battery additions in 2024, accounting for 5 GW of the 8.6 GW, Willette said. Each region is expected to install 2.5 GW of capacity in 2024. Other strong markets include Northwest Power Pool and the Desert Southwest, accounting for 1.2 GW and 0.75 GW, respectively.
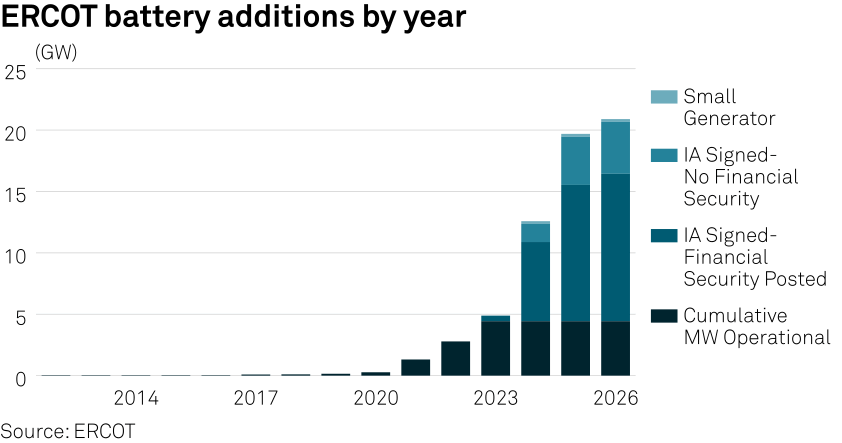
ERCOT, which manages about 90% of the state’s electric load, expects battery capacity to jump 157% in 2024 to 12.6 GW, according to its latest Capacity Changes by Fuel Type Chart.
California currently leads the US in battery storage capacity with 6.821 GW by the end of third quarter 2023, up 18% quarter on quarter, followed by Texas with 2.972 GW, up 25.3% quarter on quarter, according to American Clean Power Association. Twelve states had more than 100 MW of capacity, while 30 states had less than 100 MW. Eight states have no battery storage capacity.
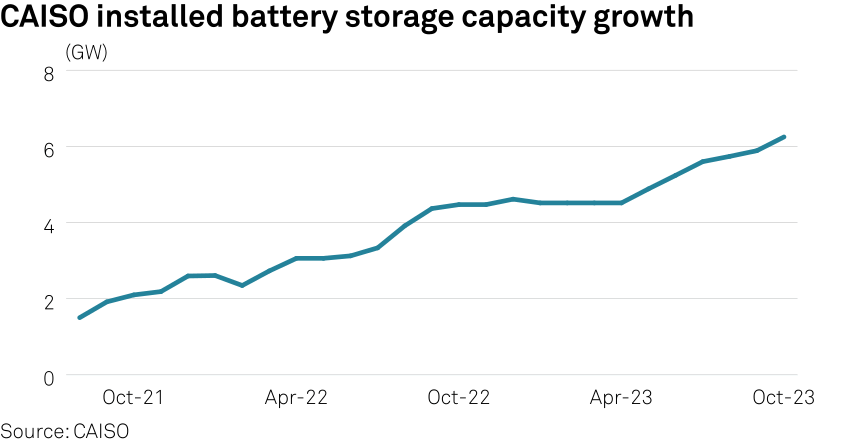
The California Independent System Operator, which manages about 80% of the state’s electric load, currently had 6.249 GW of installed battery capacity, a 40% increase from a year ago. There are over 13.4 GQW of storage projects in the CAISO interconnection queue with listed 2024 online dates, and 3.6 GW of that have executed interconnection agreements.
Quarterly record
US energy storage installations reached a new record, installing the most capacity in a quarter to date with 7.322 GWh as these became operational in the third quarter of 2023, the ACP announced Dec. 13.
“Energy storage deployment is growing dramatically, proving that it will be essential to our future energy mix,” ACP Chief Policy Officer Frank Macchiarola said in a statement. “With another quarterly record, it’s clear that energy storage is increasingly a leading technology of choice for enhancing reliability and American energy security. This industry will serve as the backbone of our modern grid. As we continue to build a strong domestic supply chain, streamlined permitting and evolving market rules can further accelerate the deployment of storage resources.”
By the end of Q3, there were 21.445 GW in the battery storage under construction or in advanced development, a 50% increase from a year ago, according to ACP. California leads with 9.331 GW under development, followed by Texas with 3.173 GW and Arizona with 2.481 GW.
Overall, 29 states have battery storage capacity under development, with seven states surpassing the 500 MW milestone, according to ACP.
Zdroj: www.spglobal.com
 En
En Cs
Cs